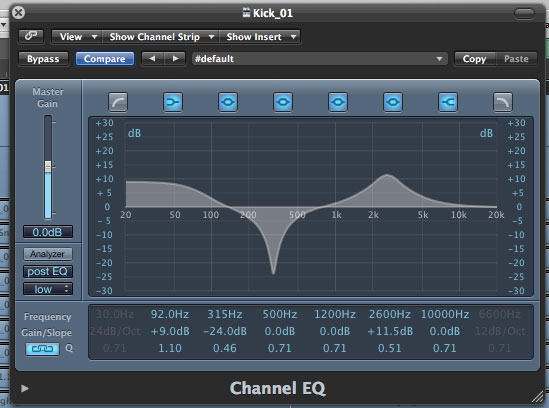
Equalization, or EQ, is the process of adjusting the balance of frequency components within an electronic signal. This is done by boosting or cutting specific sound frequencies to get a cleaner sound. For each instrument there are frequency ranges that are not needed. Equalization is so important because when frequency ranges of different instruments overlap, they clash, resulting in a “muddy” mix that doesn’t sound great. The ears of music producers and sound engineers are trained to hear and isolate frequency. The average music listener doesn’t notice or pay attention to frequency but could notice the difference between a song that has equalization and one that does not. There are five basic filter types of EQ that manipulate frequency. A low pass filter will cut out the remaining frequencies above where it is set, letting the low end of the frequencies pass. A high pass filter does just the opposite, letting only the high end through. Low and high shelves adjusts the loudness of low or high frequencies without adjusting the opposite end. Last but not least, a peak filter simply lets you accurately boost or cut one specific frequency.